Photo by <a href="https://unsplash.com/@aelwenn42" rel="nofollow">Caroline Eymond Laritaz</a> on <a href="https://unsplash.com/?utm_source=hostinger&utm_medium=referral" rel="nofollow">Unsplash</a>
Share this content:
Introduction to 3D Printing
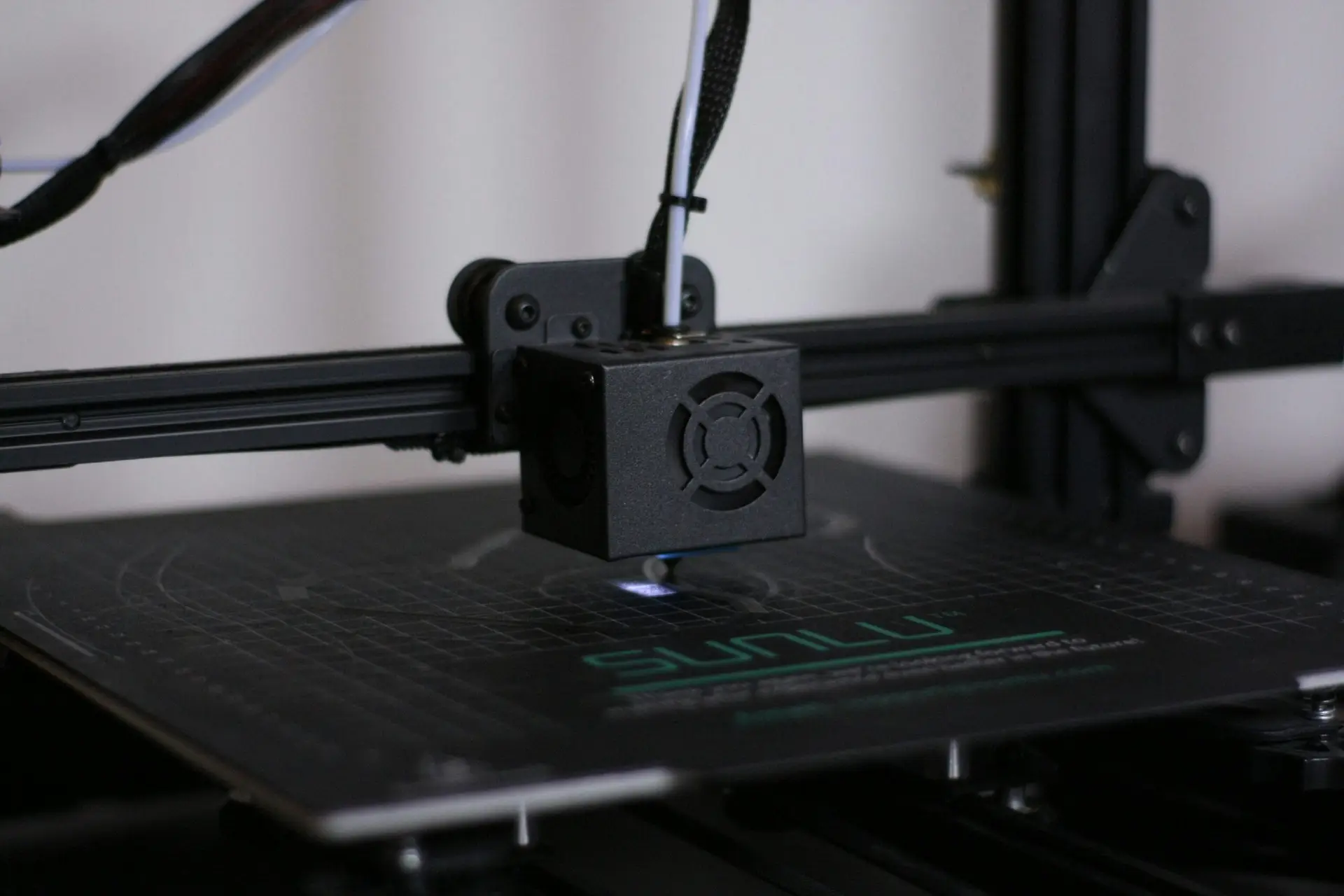
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a revolutionary technology that builds three-dimensional objects from digital files. The process begins with the creation of a 3D model using computer-aided design (CAD) software, which is then translated into a format compatible with 3D printers. The technology functions by layering materials, such as plastics, metals, or even food, to create the desired shape, offering an unprecedented level of design flexibility and customization.
The evolution of 3D printing can be traced back to the early 1980s, with its initial applications predominately in industrial contexts, such as prototyping and product development. Early adopters recognized the potential of 3D printing to reduce time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. However, in recent years, technological advancements and decreasing costs have driven the adoption of 3D printers into the home environment. Today, a wide range of affordable printers is available, catering to enthusiasts, educators, and creatives alike.
This increasing accessibility has transformed 3D printing into a hobbyist’s dream. Individuals can now easily produce anything from intricate jewelry to functional mechanical parts with minimal effort. The growing interest in 3D printing has also fostered vibrant online communities where enthusiasts share designs, tips, and experiences. Consequently, 3D printing is not only seen as a tool for personal expression but also as an innovative means of problem-solving in various sectors, including education, healthcare, and engineering.
Overall, the relevance of 3D printing in today’s technology-driven world cannot be overstated. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications will likely expand, offering even greater opportunities for innovation and creativity for individuals and businesses alike.
Types of 3D Printers
3D printing technology has advanced significantly, offering various types of printers tailored to different needs and applications. The most common types include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Understanding their operational mechanisms, strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases can assist potential users in selecting the best option for their specific requirements.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is one of the most widely used types of 3D printers, especially among hobbyists and home users. FDM printers work by melting thermoplastic filament and depositing it layer by layer to create the final object. The primary benefit of FDM technology is its cost-effectiveness and the wide variety of materials available, including PLA and ABS. However, FDM printers may not offer the same level of detail and smooth finish as other types, making them less ideal for intricate designs.
Stereolithography (SLA) uses a different approach, employing a laser to cure liquid resin into solid plastic. This technology allows for high precision and intricate details, making it suitable for applications such as jewelry design and dental modeling. Despite its accuracy, SLA printers typically have higher operating costs and require post-processing, which may deter some users. Additionally, the materials used can be more limited compared to FDM printers.
Select Laser Sintering (SLS) encompasses a more advanced technology where a laser fuses powdered material, usually nylon, to create strong and durable parts. SLS is known for producing complex geometries and functional prototypes, but it tends to be more expensive and predominantly used in industrial applications.
In conclusion, each type of 3D printer offers unique advantages and limitations. When selecting the most suitable type for home use, users should consider factors like budget, desired application, and the complexity of the items they wish to produce.
Key Features of Home 3D Printers
When selecting a home 3D printer, several key features must be considered to ensure the device meets personal projects’ requirements and users’ skill levels. Understanding these specifications will help potential buyers make informed decisions that enhance their 3D printing experiences.
Firstly, one of the principal considerations is the build volume. This parameter determines the maximum size of the object that can be printed. It varies significantly across different models, often categorized into small, medium, and large formats. For hobbyists focused on creating miniatures, a smaller build volume may suffice, whereas those interested in larger projects would benefit from printers with more extensive capabilities.
Print speed is another crucial attribute. Measured in millimeters per second (mm/s), it influences how quickly a model can be completed. While faster print speeds can be appealing, they may sometimes compromise the quality of the final output. Therefore, finding a balance between speed and quality is essential, especially for intricate designs.
Material compatibility is also vital. Home 3D printers support various filament types, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and flexible options, each with unique characteristics. Users should choose a printer that accommodates the materials required for their projects, ensuring versatility and a wider range of applications.
Resolution or layer height, measured in microns, affects the detail and smoothness of printed items. A lower micron count generally leads to finer detail but may increase printing time. Understanding one’s project requirements can aid in determining the appropriate resolution needed for satisfactory results.
Lastly, the user interface is critical, especially for beginners. A printer equipped with a straightforward touchscreen or user-friendly software can significantly enhance the overall printing experience. In summary, evaluating these key features—build volume, print speed, material compatibility, resolution, and user interface—will help in selecting the ideal home 3D printer tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Top Platforms for 3D Printing Content Creation
When it comes to creating 3D models for printing, several platforms stand out due to their unique features and varying levels of complexity. Each platform caters to different users, from beginners to advanced designers, making it essential to choose the right tool based on one’s skill set.
Tinkercad is often heralded as one of the best entry-level tools for 3D printing. This user-friendly, browser-based application enables beginners to easily create and modify 3D designs with its simple drag-and-drop interface. Tinkercad is ideal for those who are new to 3D printing, as it offers a variety of tutorials and community support. Its accessibility makes it a popular choice in educational settings, where users can quickly learn the basics of 3D modeling.
On the other hand, Blender is a more advanced, open-source platform that offers powerful tools for 3D design and animation. While it has a steeper learning curve compared to Tinkercad, Blender’s extensive capabilities allow for intricate designs, including sculpting, texturing, and rendering. This makes Blender suitable for users who have some experience in 3D modeling and are looking to create more detailed and complex projects.
Fusion 360, developed by Autodesk, strikes a balance between accessibility and advanced features. It provides a robust set of tools for professional-grade design, engineering, and simulation, making it an excellent choice for hobbyists and professionals alike. Fusion 360 is particularly suitable for those who seek a combination of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) capabilities. With its cloud-based system, collaboration with other users is also straightforward, adding to its appeal for team projects.
In conclusion, the choice of platform for 3D printing content creation largely depends on the user’s experience level and specific project requirements. By evaluating each of these tools, individuals can select the one that aligns best with their capabilities and goals. Whether a user opts for the simplicity of Tinkercad or the sophisticated features of Blender or Fusion 360, each platform offers valuable opportunities to dive into the world of 3D printing.
Durability and Affordability of 3D Printers
When considering a 3D printer for home use, durability and affordability emerge as crucial factors. The market offers a range of options that cater to varying budgets while delivering reliable performance. Identifying a printer that combines high durability with an attractive price point can be pivotal for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Several brands are renowned for producing durable 3D printers. For instance, Prusa Research has established a reputation for offering high-quality printers that withstand the test of time. Their Prusa i3 MK3 model is widely regarded as one of the best in its class, combining a robust build with advanced features. Similarly, Ultimaker 2+ is known for its sturdy design, making it an ideal choice for users who require a dependable machine for regular use.
On the affordability spectrum, brands like Creality and Anycubic provide commendable options that do not compromise on quality. The Creality Ender 3, for instance, is often hailed for its mix of affordability and functionality, making it accessible for beginners seeking a durable machine. Anycubic’s i3 Mega also presents a budget-friendly alternative, featuring a solid frame and user-friendly interface that appeals to both novices and experienced users.
For those prioritizing performance without overspending, some lesser-known brands are also making strides. Brands such as Artillery offer competitive pricing while maintaining solid construction and print quality. Ultimately, when evaluating durability and affordability, it is essential to assess not just the purchase price but also the potential long-term value, including maintenance costs and the availability of replacement parts. Investing in a durable printer within budget ensures a satisfactory experience, balancing both reliability and financial prudence.
Ease of Use: Beginner-Friendly 3D Printers
For those new to the world of 3D printing, selecting a user-friendly machine is crucial. With the variety of options available, beginner-friendly 3D printers stand out due to their noteworthy features such as straightforward setup processes, quality support resources, and intuitive interfaces. These qualities are fundamental in ensuring new users transition smoothly into the multifaceted sphere of 3D printing.
Several leading brands have developed beginner-oriented 3D printers that minimize technical barriers. For example, printers like the Creality Ender 3 or the Anycubic i3 Mega are often praised for their assembly simplicity. Many of these printers come mostly pre-assembled or require only a few screws to secure different parts, making the initial setup less daunting for novices. Furthermore, many manufacturers provide comprehensive guidance videos, detailed manuals, and online forums that foster an engaging environment for beginners seeking assistance and community support.
Another vital aspect to consider when choosing a beginner-friendly 3D printer is the user interface. An EASY-TO-NAVIGATE touch screen or a clear LCD display enhances the experience by simplifying control functions and aiding in the navigation of settings. Printers with reproducible print quality and reliable hardware help beginners produce impressive results, contributing to their satisfaction and confidence in pursuing 3D printing projects.
To acclimate to the 3D printing process, newcomers should start with simple designs and gradually tackle more intricate models. Utilizing reputable slicer software, which often comes bundled with the printer, allows users to modify and prepare their designs effortlessly. Engaging with online tutorials and community groups will further enhance their skills and knowledge. By approaching with patience and curiosity, new users can enjoy a fulfilling introduction to 3D printing technologies.
Latest Trends in 3D Printing Technology
The field of 3D printing technology is continuously evolving, marked by exciting advancements and trends that shape how individuals and businesses utilize this powerful tool. One of the most significant trends is the development of new materials. Innovations in filament types, such as biodegradable plastics and metal-infused materials, have expanded the range of applications for 3D printing. These materials provide enhanced strength and durability, allowing for more complex and functional designs in everyday objects.
Moreover, the evolution of innovative printing techniques has contributed to the efficiency and capabilities of 3D printers. Techniques such as multi-material printing and continuous filament fabrication (CFF) are gaining traction. These methods enable users to create intricate structures with varying properties, paving the way for more sophisticated products. As a result, the barriers that once limited 3D printing applications are gradually diminishing.
Another noteworthy trend is the democratization of 3D printing technology. With the proliferation of affordable and user-friendly 3D printers, individuals from diverse backgrounds are able to engage in this creative process. This accessibility has ushered in a new era where hobbyists and small businesses can explore custom designs and production, thereby stimulating innovation across various sectors.
In line with this surge in accessibility, eco-friendly practices in 3D printing are also emerging. The industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability, exploring ways to reduce waste and minimize the environmental footprint of 3D printing. Companies are investing in recycled materials and developing processes that utilize fewer resources while maintaining high-quality outputs.
Furthermore, emerging markets worldwide are leveraging 3D printing technology for unique applications, ranging from healthcare innovations to customized manufacturing solutions. This versatility underscores the potential of 3D printing to address specific needs across various industries, making it an integral part of future technological advancements.
Real-World Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing technology has evolved significantly in recent years, leading to a multitude of practical applications across various sectors. One prominent arena is education, where 3D printers serve as tools for enhancing learning experiences. Educational institutions can utilize 3D printing to facilitate interactive projects, allowing students to create tangible models and prototypes that elucidate complex concepts. This hands-on approach not only fosters creativity but also engages students in critical thinking and problem-solving.
In the healthcare sector, 3D printing has made remarkable strides, offering innovative solutions that can lead to improved patient outcomes. Medical professionals have begun using 3D-printed anatomical models for pre-surgical planning, providing a clear visual representation of the patient’s unique physiology. Furthermore, 3D printing enables the production of custom prosthetics and implants, tailored specifically to fit individual needs. This personalization promotes better comfort and functionality for patients, showcasing the technology’s potential in transforming healthcare delivery.
The manufacturing industry has also embraced 3D printing, recognizing its capacity for streamlining production processes and reducing costs. Companies are leveraging additive manufacturing to create complex parts with minimal waste, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. Additionally, 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling businesses to test and iterate designs swiftly before committing to mass production. This flexibility leads to quicker turnaround times and fosters innovation in product development.
Finally, on a more personal level, 3D printing has opened up a world of possibilities for home projects. Enthusiasts are utilizing this technology to create customized decor, household items, and tools that cater to specific needs and preferences. The ability to design and print objects on-demand empowers individuals to tackle DIY projects more effectively, further demonstrating the versatility of 3D printing in the modern era.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In summary, the world of 3D printing has expanded significantly, offering a variety of options tailored for home use. Aspiring users need to consider several key factors, including the type of materials they wish to use, the complexity of projects they intend to undertake, and their budget constraints. Each 3D printer category, such as FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), SLA (Stereolithography), and DLP (Digital Light Processing), presents unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for aligning a printer with personal interests and project goals.
For newcomers to 3D printing, an FDM printer is often recommended due to its accessibility, affordability, and ease of use. They are widely available in various price ranges, making them suitable for hobbyists and those looking to experiment without a significant financial commitment. Quality entry-level models can produce impressive prints, allowing users to engage creatively without overwhelming technical challenges.
On the other hand, users with specific requirements, such as intricate details and a smoother finish, may lean towards SLA or DLP printers, despite their typically higher costs and maintenance demands. These printers excel in producing high-resolution prints that might be essential for certain applications, like miniatures or prototypes. Overall, it is vital to examine not only the technical specifications but also post-processing needs and community support, which can significantly enhance the user experience.
Ultimately, making an informed decision involves carefully weighing individual needs against the options available. It is advisable to read reviews, compare different models, and even consult user forums when selecting a 3D printer. By doing so, readers can ensure that their first investment in 3D printing technology will align perfectly with their intended use, skills, and aspirations, leading to a satisfying and successful journey in the realm of 3D printing. Investing in a 3D printer for home use opens up a world of creative possibilities. The Creality Ender 3 V3 SE, Bambu Lab A1 Mini, and Flashforge Adventurer 5M are excellent choices that offer a blend of durability, affordability, and user-friendly features. Pairing these printers with intuitive software platforms like Tinkercad, Blender, or SketchUp can further enhance your 3D printing experience, making it both enjoyable and productive.
Top 3D Printers for Home Use
1. Creality Ender 3 V3 SE
The Creality Ender 3 V3 SE stands out as an exceptional budget-friendly FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printer. Priced at approximately $219, it offers features typically found in higher-end models, including:
• Automatic bed leveling with CR Touch.
• Sprite direct drive extruder.
• Maximum printing speed of 250 mm/s.
Its build volume of 220 x 220 x 250 mm is ample for most home projects. The printer’s ease of assembly and user-friendly interface make it ideal for beginners. However, it lacks Wi-Fi connectivity, relying on an SD card for file transfers.
2. Bambu Lab A1 Mini
For those interested in multicolor printing, the Bambu Lab A1 Mini is a compelling choice. Available at $199 for the standalone printer and $349 for the combo with AMS Lite, it allows printing with up to four colors using PLA and PETG filaments. Key features include:
• Fast printing capabilities.
• Quiet operation.
• User-friendly assembly process.
This printer is particularly suitable for users looking to explore multicolor 3D printing without a steep learning curve.
3. Flashforge Adventurer 5M
The Flashforge Adventurer 5M is recognized for its user-friendly design and reliability. While specific features and pricing details are limited in the available sources, it is mentioned as a good budget option that is user-friendly.
Top 3D Modeling Software Platforms
Selecting the right software is essential for designing and preparing models for 3D printing. Here are some top recommendations:
1. Tinkercad
Developed by Autodesk, Tinkercad is a free, browser-based 3D modeling tool ideal for beginners. It employs a simple block-building approach, allowing users to create models by combining primitive shapes. Its intuitive interface makes it accessible for users of all ages.
2. Blender
Blender is a powerful, open-source 3D modeling software suitable for both beginners and professionals. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools for modeling, sculpting, and rendering. While it has a steeper learning curve compared to Tinkercad, its capabilities are extensive, making it a favorite among many 3D artists.
3. SketchUp
SketchUp provides a balance between usability and functionality, making it suitable for most skill levels. It is especially good for designing interior and exterior architectural projects but also has tools for a diverse range of other purposes.